We examine the leading 10 applications of blockchain technology across financial services, insurance, global trade, sustainability, healthcare, and government today.
Blockchain technology has existed for several years, originating with the launch of the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, in 2009 by the mysterious figure Satoshi Nakamoto.
This technology has supported the creation of numerous other cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, and has led to variations in digitally traded assets, including stablecoins and dogecoins.
These alternative currencies derive their nature from the blockchain on which they are created. As the understanding of the technology has evolved, its use cases today are diverse, with many additional applications yet to be discovered.
What exactly is blockchain?
In simple terms, blockchain serves as a shared, open, and unchangeable ledger that aids in recording transactions and monitoring assets within a business network.
At its essence, blockchain technology promotes transparency, immutability, automation, and decentralization.
For numerous organizations across various sectors, the principle of decentralization translates into trust in the technology, as all transactions are accessible to every participant on the same chain.
As trust has developed and knowledge of the technology has expanded, the adoption of blockchain has flourished.
Here, we explore the Top 10 applications of blockchain technology today.
Capital Markets
Blockchain technology is being examined in capital markets through several significant avenues. It can facilitate easier, more economical, and quicker access to capital when utilized properly. In trade settlement and clearing processes, blockchain can support near real-time settlements while minimizing the necessity for middlemen. Its unchangeable ledger also reduces settlement risk.
Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate the execution of derivative contracts based on predetermined conditions and can streamline dividend distributions. Notably, it can transform traditional assets like stocks and bonds into digital securities, enabling fractional ownership.
CBDCs
Blockchain can also support Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) – a digital version of central bank money that presents unique benefits for central banks at both retail and wholesale levels, ranging from improved financial access for individuals to increased efficiency in infrastructure for intermediate settlements.
Utilizing distributed ledger transactions (DLT), CBDCs can be issued, documented, and verified in a decentralized manner. An unchangeable ledger ensures transparency for tracking the issuance and movement of CBDC transactions. Blockchain-based CBDCs also empower central banks to regulate currency supplies without sacrificing user privacy and security. Furthermore, they are programmable, allowing for hard-coding rules such as wallet limits or third-party access into the protocol.
Financial Services
Conventional financial services face challenges stemming from outdated processes, security concerns, and sluggish payment settlements. By employing blockchain technology as the foundational framework, financial services providers can optimize payments and money transfers to achieve quicker, cheaper, and more secure transactions, both domestically and internationally. Financial service providers can operate without the need for intermediaries, such as banks, when using blockchain to expedite money movement.
The enhancement of financial instruments is possible through blockchain technology, which increases liquidity while lowering capital costs and mitigating counterparty risk.
DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to the transition from traditional centralized financial frameworks to peer-to-peer finance enabled by decentralized technologies rooted in Ethereum. DeFi stands out as one of the most prevalent applications of blockchain technology today, with millions engaging in this innovative financial ecosystem that provides enhanced financial access and support.
Prominent DeFi examples include decentralized exchanges, which utilize blockchain smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies and tokens, alongside lending and borrowing platforms that allow users to lend or borrow cryptocurrencies without relying on traditional financial entities.
Digital Identity
Blockchain technology is also becoming increasingly important in the realm of cybersecurity. Regarding digital identities, blockchain facilitates the notion of self-sovereign identity (SSI), where individuals maintain complete control and ownership over their digital identities and personal information. Instead of depending on centralized authorities like companies or governments to issue and manage identities, blockchain permits users to establish and control their own identities. The use of SSI is anticipated to grow in 2024.
Moreover, blockchain supports decentralized identifiers (DIDs) – unique identifiers that are globally resolvable and linked to a decentralized identity record stored on the blockchain. DIDs enable individuals to demonstrate control over their digital identity without depending on centralized registries.
Insurance
Fraud is prevalent in the insurance claims process, and claim evaluations can take a long time. By utilizing blockchain technology, insurers can enhance data verification, streamline disbursements, and expedite claims processing—thereby shortening the time needed for claims and reducing costs. Additionally, by using blockchain, insurers can create a reliable and unchangeable record of high-value insured items regarding their provenance, ownership history, and warranty claims. This fosters transparency and helps to further prevent claims fraud.
The processes for Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) can also see improvements as blockchain enables insurers to minimize redundant efforts and enhance regulatory oversight.
Global Trade & Commerce
Currently, blockchain is being investigated to digitize trade documentation and simplify traditionally complex processes like letters of credit, while ensuring a tamper-proof environment for secure trade finance transactions. The issuance of letters of credit can now be executed through smart contracts that rely on the satisfaction of pre-defined conditions, all thanks to blockchain technology.
In terms of supply chains, blockchain can transparently generate a record detailing a product’s origin, ownership history, and its trajectory throughout the supply chain. For instance, initiatives like IBM’s Food Trust and Walmart’s blockchain solution facilitate the immutable tracking of produce from farm to store—ensuring compliance with ethical sourcing and food safety regulations.
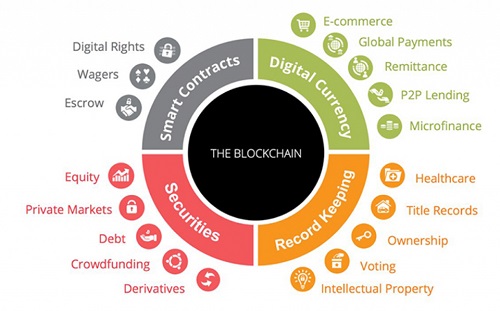
Sustainability
In the realm of sustainability, blockchain technology is enabling organizations to make significant advancements, especially within the energy sector. It allows for peer-to-peer trading of renewable energy, enabling individuals and businesses to engage in energy transactions without intermediaries or grid operators, which leads to a more efficient and cost-effective energy market that maximizes the use of renewable energy sources. Projects such as Brooklyn Microgrid could enable distributed energy resources to fulfill up to 45% of global electricity demand by 2050.
Moreover, smart grid management can be efficiently and securely handled via blockchain, allowing for transparent oversight of energy demand, supply, and data flows in smart grids. Features for tracking carbon emissions are also achievable through organizations that are leveraging blockchain technology.
Healthcare
The influence of blockchain has quickly expanded, and it is now supporting healthcare providers in utilizing decentralized electronic health records (EHRs). By establishing a permanent audit trail, blockchain technology guarantees the integrity of all modifications made to a patient’s medical history.
Blockchain can also securely store credentials, certifications, and licenses for healthcare providers on a distributed ledger, aiding in verification processes and reducing the risk of forgeries.
Government & Public Sector
Blockchain’s application extends beyond private sectors; it is also under exploration in the public sector and within governmental bodies. Identity management and citizen records enhanced by blockchain are aiding in the prevention of fraud, data tampering, and unauthorized access. In the U.S., initiatives such as the Illinois Blockchain Initiative and Delaware’s effort for archiving public records are examples.
Additionally, blockchain is being utilized for land and property registration, supporting electoral processes and enhancing public service delivery.
Enterprise blockchains are transforming data management, providing scalability and security while facilitating real-world applications beyond mere speculation.
People often inquire about what I mean by “enterprise blockchain” and how it differs from other types of blockchains. The distinction lies in the purposes for which a blockchain is used and what it can potentially achieve. Not all blockchains are the same.
For more than ten years, blockchains have primarily been viewed as platforms for digital currencies and speculative investment tools.
Certain blockchains—like those that support decentralized finance (DeFi) applications—concentrate on staking or lending assets for profit, creating a chain of interdependencies that have historically been problematic.
In contrast, enterprise blockchains provide unlimited scalability, enabling them to manage data-heavy tasks that can overwhelm networks with limited bandwidth. The technology behind enterprise blockchains strikes a balance between efficiency and transparency, allowing companies to grow without compromising on security or the ability to audit transactions.
Enterprise blockchains offer the technical framework necessary to manage agreements related to intellectual property, development and training of AI, micropayments, and much more in a streamlined and auditable manner.
These are not just theoretical ideas—there are already existing real-world applications that demonstrate enterprise blockchains extend beyond speculative uses.
Addressing the issue
Think about copyright management, which is increasingly important as AI language models (LLMs) indiscriminately scrape the internet, disregarding data owners’ rights. Non-fungible token (NFT) technology based on enterprise blockchains can help ensure that right holders receive compensation for their content.
Many people dismissed NFTs in the past, having been led to believe the technology was solely about the speculative trading of poorly designed monkey JPEGs. However, NFTs can be employed in self-executing smart contracts that regulate the usage, resale, and licensing of data.
The NFT is constructed using Bitcoin Script, a Turing-incomplete programming language that can verify whether the terms of a contract have been fulfilled. For an LLM accessing material, the contract can stipulate the terms, including the duration of access, permitted uses of the data, and required payments to compensate the material’s owner.
Enterprise blockchains create verifiable trails that timestamp interactions with copyrighted material. Every time AI systems utilize on-chain content, the actions are recorded and remain auditable by regulators, content producers, and AI developers.
Overlay networks and payment channels
Enterprise blockchains facilitate adaptive and flexible interactions through overlay networks and payment channels. Overlays are additional systems constructed on top of the main network, managing off-chain negotiations and updates until the final settlement occurs.
Overlays allow for customizable, real-time agreements between businesses and AI systems. Content providers, for instance, may offer tiered pricing based on whether an AI system merely requires reading data, deeper integration into training models, or the ability to resell or modify content.
Payment channels consolidate several interactions into a single, secure on-chain settlement, ensuring the effective use of enterprise blockchain resources while maintaining complete auditability.
For instance, an AI developer and a content provider can establish a payment channel on the main network, securing a portion of a blockchain’s native token. The two parties negotiate terms off-chain, adjusting the balance within the channel based on the volume of content accessed or utilized. Once the business concludes, the payment channel is closed, and a final settlement transaction is recorded on the main network, creating an auditable and unalterable record of their agreement.
Truly outstanding
I contend that the BSV Blockchain uniquely possesses the capability to securely and efficiently handle the aforementioned scenarios. BSV delivers limitless scalability—proven to accommodate over one million transactions per second—with transaction fees amounting to mere fractions of a cent.
BSV is also the sole chain capable of scaling to comply with the IPv6 standard, which is essential for managing the enormous data needs of Metanet, set to merge with AI and machine learning to facilitate cost-effective, instantaneous micropayments. Metanet signifies a more effective, inclusive, and dynamic internet, an economically integrated system that reinstates the original vision of a peer-to-peer internet framework.
I firmly believe in BSV’s distinct qualities and challenge anyone developing comparable projects on other blockchains to showcase their work at the London Blockchain Conference (LBC) in 2025. To paraphrase some of my football-loving friends from England, step up if you think your blockchain can compete.
In all seriousness, this is a genuine invitation. Throughout my extensive entrepreneurial career, I have remained open to defending my perspectives in the field of free market competition. The next LBC is slated for October 2025, offering ample time to prepare a presentation that will impress everyone.
Assuming your foundation is an authentic enterprise blockchain capable of processing millions of cost-effective transactions each second. However, if that foundation turns out to be unstable, you can always migrate your project to BSV and consider the initial attempt a prototype.
Sandcastles may appear beautiful but they don’t endure for long. Select the enterprise blockchain that is designed to excel and endure over time.
How universities can leverage blockchain to revolutionize research
Picture a situation where you’re a professor at a research university about to advance in your research project. Just as you’re ready to delve deeper, you realize you need a substantial data set from the previous year’s research.
Assuredly, you reach out to your data storage provider for access, only to be caught off guard by an unexpected fee known as an egress charge. This was neither anticipated nor factored into your budget; what course of action do you take? Depending on the data set’s size, egress fees can be excessively expensive.
This predicament is not isolated but a common issue faced by university professors and researchers around the world. Acknowledging these data-related challenges, academic institutions are beginning to adopt new technologies to resolve them.
One technology that is gaining momentum at universities is blockchain. Blockchain represents a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that spreads data throughout a network. The increasing adoption of blockchain technology by academic institutions is fueled by advancements in decentralized storage solutions that promise more affordable and secure data storage for large-scale research projects.
This investigation is becoming increasingly pertinent in response to the urgent need to safeguard vital research data. Furthermore, this approach highlights the opportunity to alleviate vulnerabilities and inefficiencies associated with centralized storage models, including the risks of data loss and limitations resulting from costly egress fees.
How blockchain technology can benefit higher education
Research universities are progressively exploring the advantages of blockchain technology.
Recognized for its capability to offer a secure and efficient method of immutable record-keeping, blockchain presents promising opportunities for improving efficiency, security, and credibility within higher education.
Its distributed ledger technology provides a revolutionary approach to managing and validating digital information. One significant application is the management of educational credentials.
Blockchain would improve accessibility for learners, institutions, and employers alike. By dismantling geographical and institutional barriers, blockchain ensures that credentials are recognized globally and can be validated instantly by educational organizations worldwide.
Educational credentials are closely linked to the concept of data democratization. Data democratization refers to the capacity to share extensive data sets among institutions and researchers around the world.
By utilizing distributed ledger technology, blockchain opens up access to massive datasets, promoting wider participation in scientific research and education.
In addition to credentials and data democratization, the implementation of blockchain in higher education could lead to considerable cost reductions, minimizing the dependence on expensive centralized systems for credential verification and data handling.
By streamlining these processes through blockchain, universities can use their resources more efficiently, potentially lowering administrative expenses and making education more accessible for students.
Blockchain’s contribution to enhancing scientific discovery
For research universities, the motivation for adopting blockchain is driven by the demand for improved security, enhanced data integrity, and easier sharing and collaboration among institutions.
Due to its decentralized nature, blockchain provides an unalterable record of data transactions, guaranteeing that once data has been recorded, it cannot be modified or tampered with.
This feature is especially beneficial for scientific research, where the authenticity and reliability of data are crucial. Moreover, blockchain-based data storage systems allow researchers to retain control over their data while providing transparent and verified access for peer review and collaborative studies.
These applications illustrate that blockchain technology is not only emerging as a secure and efficient method of data storage but also fostering a more inclusive and collaborative research environment, where knowledge is freely shared and research is collectively nurtured.
With its promise of heightened security, accessibility, and data integrity, blockchain technology is establishing a new benchmark for academic research, making higher education more interconnected than ever.
By embracing blockchain-powered storage solutions, universities can pave the way toward a more secure, inclusive, and collaborative future for academic research and education.